
menu
You are about to leave the website of Otsuka Novel Products GmbH and view the content of an external website. Otsuka Novel Products GmbH cannot be held responsible for the content of external websites.

Source: World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2024. World Health Organization, Geneva, 2024. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
Photo credit: Qilai Shen
Source: World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2024. World Health Organization, Geneva, 2024. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
Photo credit: Sergey Golovach

Source: World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2024. World Health Organization, Geneva, 2024. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
Photo credit: Riccardo Venturi

Source: World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2024. World Health Organization, Geneva, 2024. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
Photo credit: Edwin Tuyay
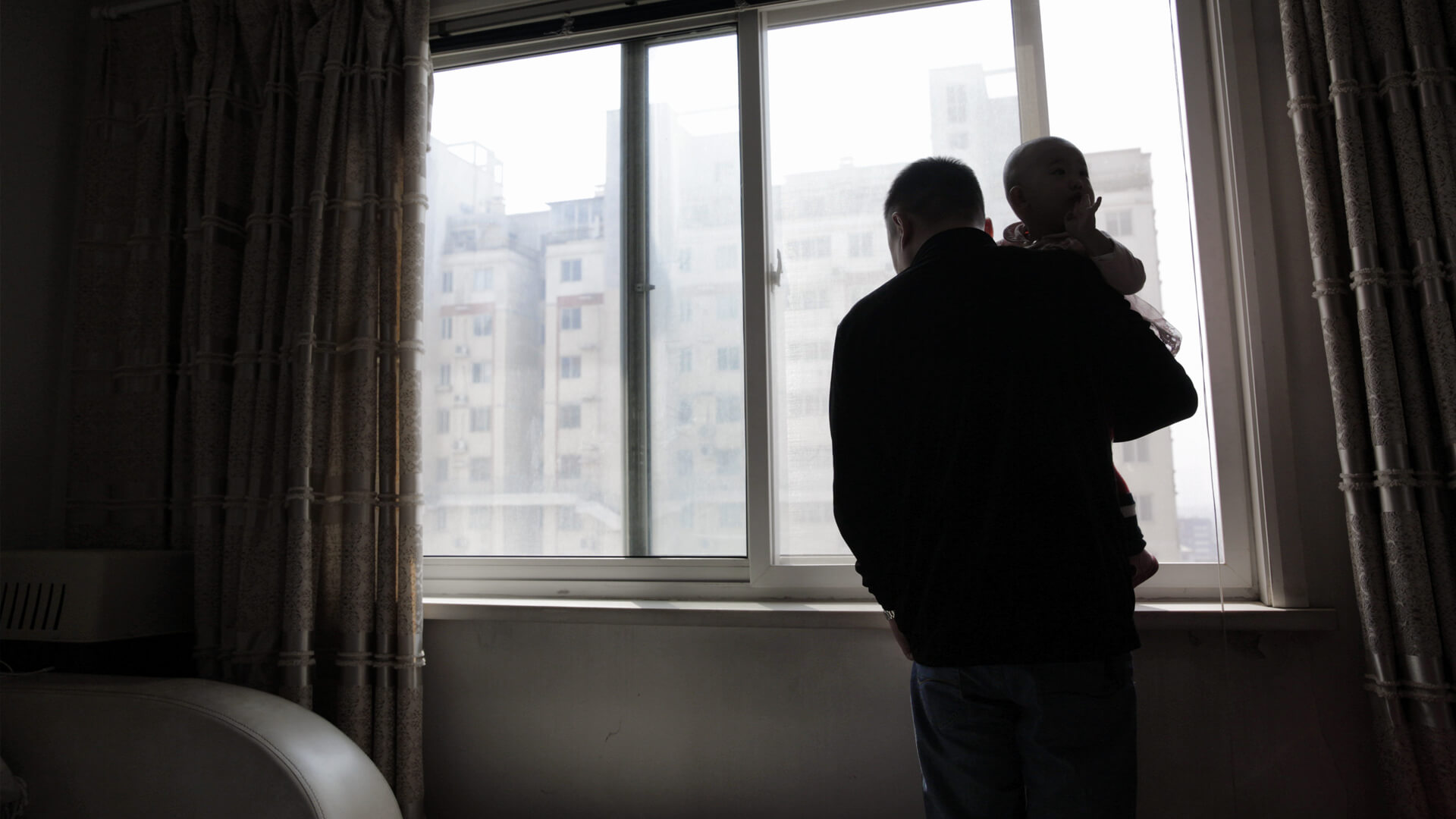

Source: World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2024. World Health Organization, Geneva, 2024. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO; World Health Organization. Tuberculosis Factsheet. Published 29 October 2024. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/tuberculosis (Accessed 19 February 2025).
Photo credit: Qilai Shen
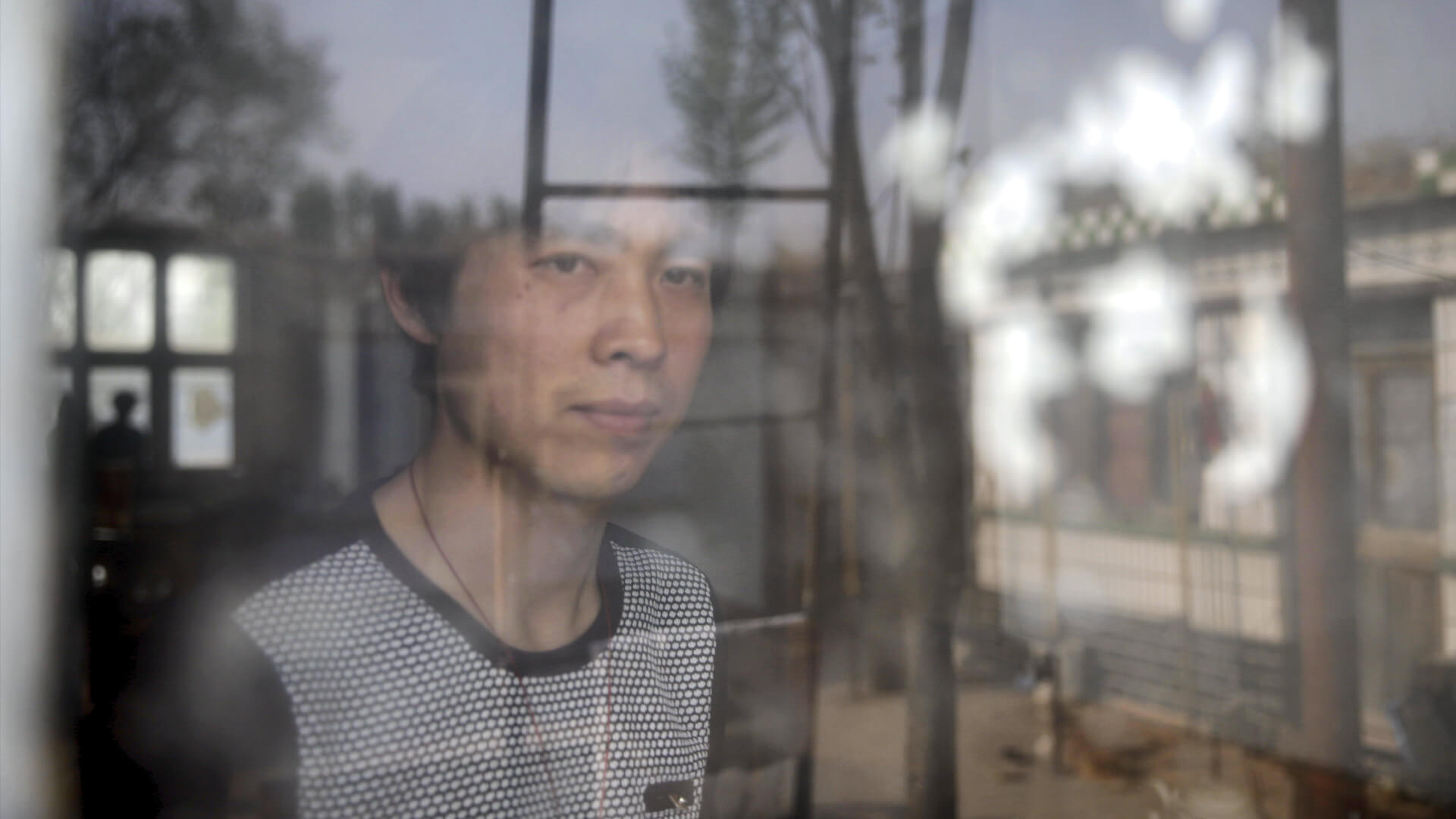

Source: World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2024. World Health Organization, Geneva, 2024. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
Photo credit: Qilai Shen
Access to Medicine Foundation. Antimicrobial Resistance Benchmark 2021. Available at: https://accesstomedicinefoundation.org/ (accessed 24 February 2025)
Photo credit: Riccardo Venturi
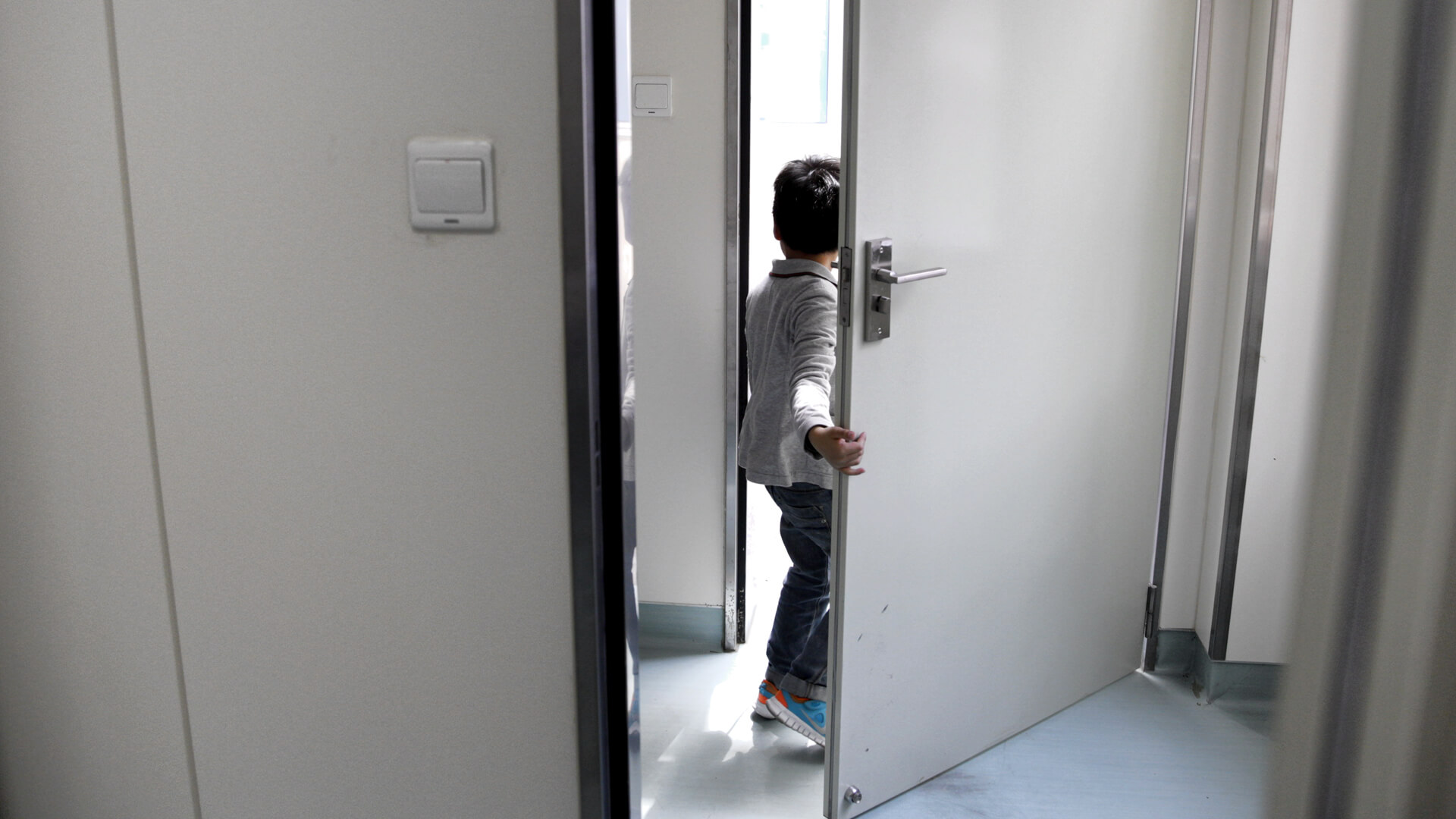

Source: Based on Treatment Action Group, Reports on Tuberculosis Research Funding Trends, issues from 2005-2023 (Accessed 24 February 2025). All reports available at: https://www.treatmentactiongroup.org/
Photo credit: Qilai Shen
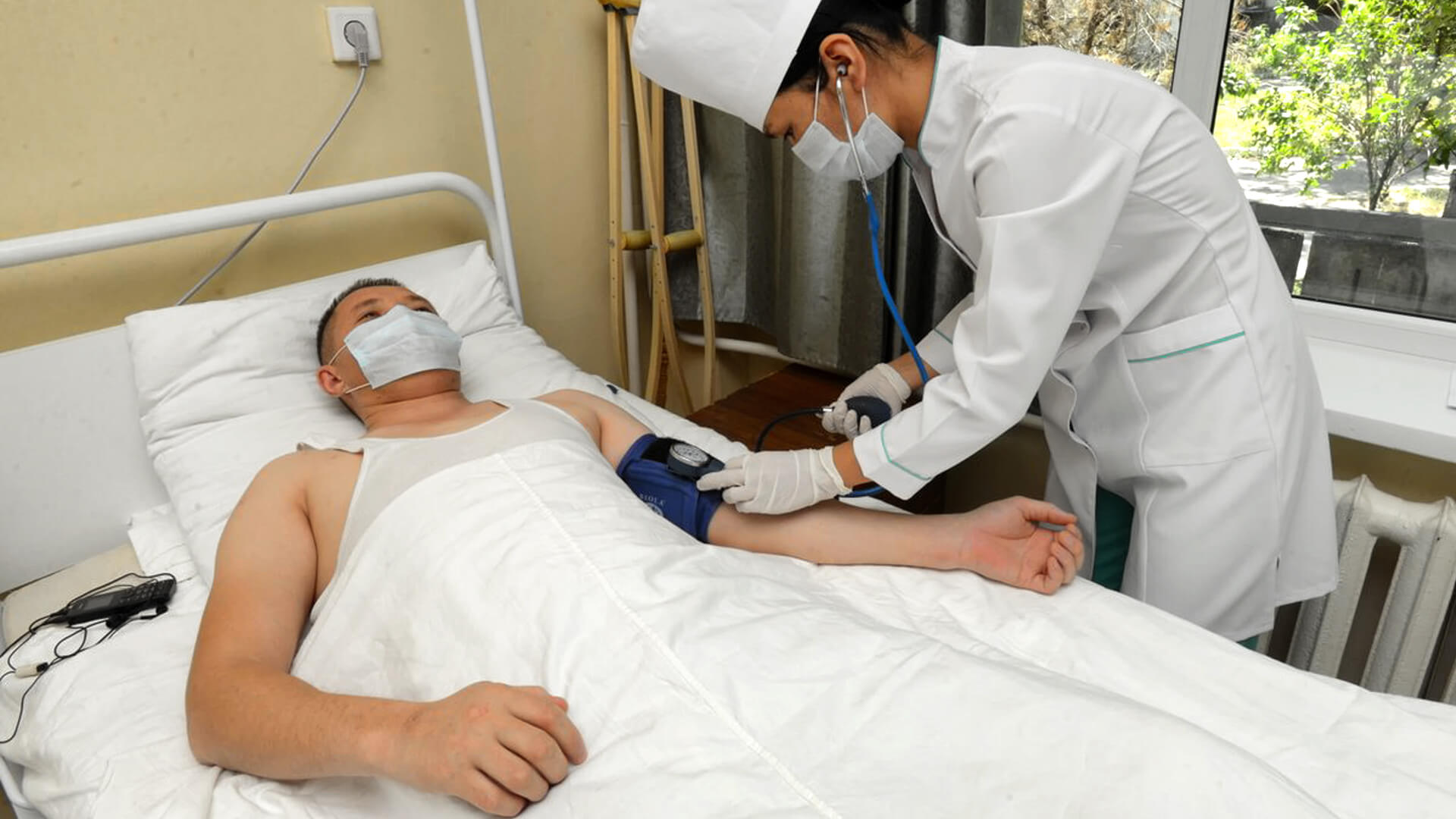
Tuberculosis (TB) is one of the oldest and most persistent epidemics, still affecting people in every country in the world. The World Health Organization estimates that in 2023, 10.8 million people became newly infected with TB, including 1.3 million children.1
TB is spread through air. It most commonly affects the lungs, but can spread to almost any part of the body. About one quarter of the world population is latently infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacteria that cause the disease. Those infected have a 5 to 10% lifetime risk of developing active TB. People with weakened immune systems, such as people living with HIV or diabetes, or people who smoke tobacco, have a much higher risk of falling ill with TB.2
The global progress in eliminating TB has been very slow. The global TB incidence rate is estimated to have increased by 4.6% between 2020 and 2023, following declines of about 2% per year between 2010 and 2020.1 TB is still one of the leading causes of death from a single infectious agent worldwide.2 In 2023 alone an estimated 1.25 million people died from this disease.1
Yet with proper management, TB is curable. However, even treatment of uncomplicated forms of TB requires taking a number of medicines every day for 4 to 6 months.2
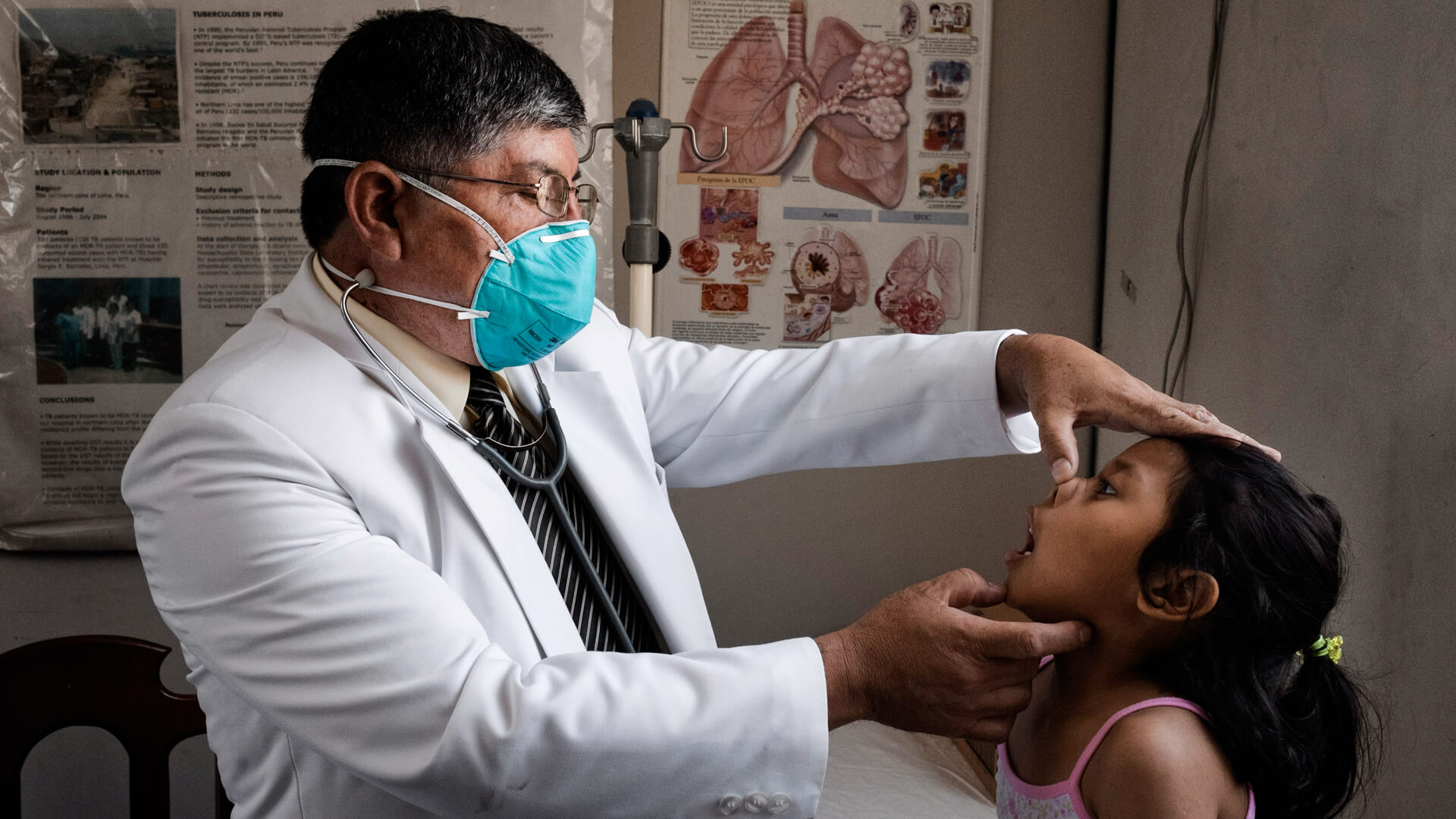
The progress in eliminating TB and curing those affected by it has been eroded by the spread of drug-resistant bacteria. To learn more about drug-resistance, click here.
Otsuka has been searching for new tools to fight TB for over 50 years, and has been one of the leading private sector funders of TB Research & Development in the world since 2005.3 It is committed to finding innovative solutions to effectively treat drug-resistant forms of TB, as well as to simplify and shorten treatment.
References
1. World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2024. World Health Organization, Geneva, 2024. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
2. World Health Organization. Tuberculosis Factsheet. Published on 29 October 2024. Available at: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/tuberculosis (Accessed 24 February 2025).
3. Based on Treatment Action Group, Reports on Tuberculosis Research Funding Trends, issues from 2006 until 2024 (accessed 24 February 2025). All reports available at: https://www.treatmentactiongroup.org/
Information current as of March 2025
Reference ONP-DEL-2500004